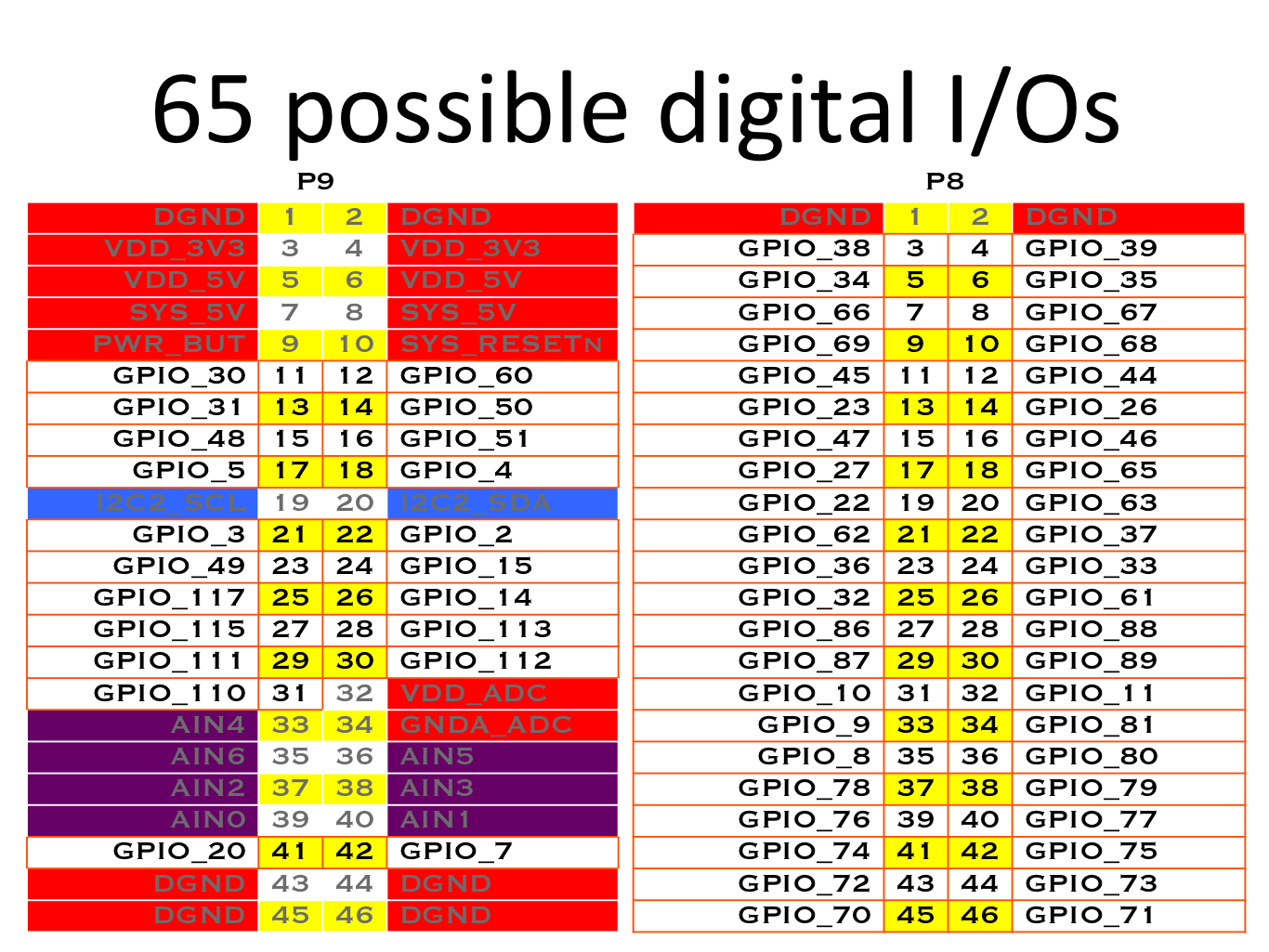
27 Feb 2015

Refer this site. This gives a fare idea about how to design a simple transistor switch. Or go to this site.
The max o/p voltage from the gpio pin is 3.3 V. But you can get a 5V VDD from Beaglebone Black board.
The circuit I designed is given below. The transistor I used is KN2222A. (You can use any transistor)
Will add a nice circuit diagram later. Once you are finished with the circuit follow the steps in this page.
cd /sys/class/gpio
echo 23 > export
cd gpio23
echo out > direction
Then save the script given below to a file and run this in your BBB. (It will blink the LED once every second.) Cntrl + C to stop the script.
The max o/p voltage from the gpio pin is 3.3 V. But you can get a 5V VDD from Beaglebone Black board.
The circuit I designed is given below. The transistor I used is KN2222A. (You can use any transistor)
Will add a nice circuit diagram later. Once you are finished with the circuit follow the steps in this page.
cd /sys/class/gpio
echo 23 > export
cd gpio23
echo out > direction
Then save the script given below to a file and run this in your BBB. (It will blink the LED once every second.) Cntrl + C to stop the script.